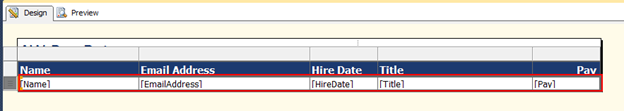
Designing a table can be a little complicated if you don’t have the correct knowledge of data types, relationships, and even column properties. In this post, I’ll go over the column properties and provide examples.
To create a new table using SSMS, expand the tree for a database and right click on Tables and select “New Table…” as shown below.
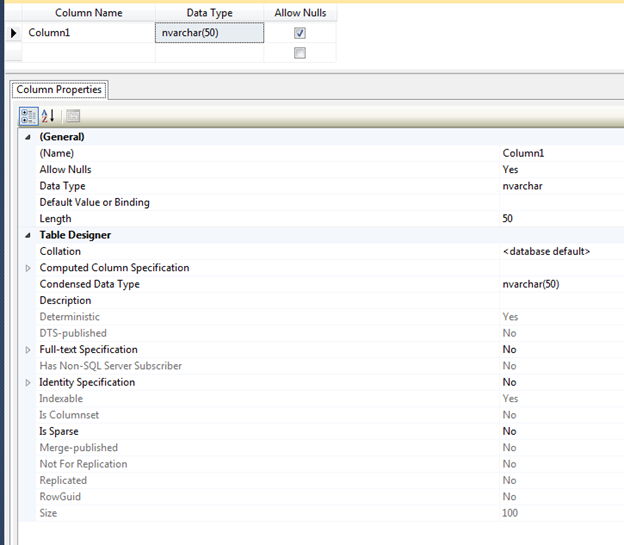
A new window will open and once you enter a Column Name and a Data Type you will see the appropriate Column Properties for that data type as shown below:
Note: Some properties only appear for certain data types
OK, let’s go over each property.
(Name)
Name, simply, is the name of the column. You can change the name of the column in the table design view or in the column properties.
Allow Nulls
Allow Nulls indicates whether or not the column will allow null values. If the column does not allow null values then some sort of data must be put into this record. You can change this value in the table design view by checking/unchecking the Allow Nulls box or from the column properties.
Data Type
Data type, like its name implies, is the type of data stored for the column. You can learn more about data types in this article. You can change the data type in the table design view or the column properties.
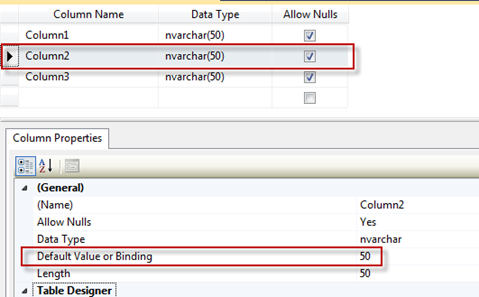
Default Value or Binding
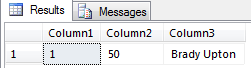
The Default Value option will allow you to enter a default value in case a value is not specified in an insert statement. For example, let’s say we have three columns in a table named Demo (Column1, Column2, and Column3) and we put a value of 50 in the Default Value or Binding for Column2.
In the query below we are inserting data to Column1 and Column3, but nothing for Column2 so this will get the default value of 50.
INSERT INTO DEMO (Column1, Column3) VALUES (1, ‘Brady Upton')
Our result set should be:
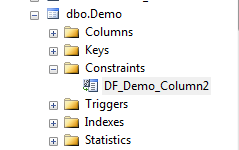
By creating a default value, this also creates a default constraint automatically as well as shown below:
Length
Length displays the number of characters for character-based data types. For example, nvarchar(50) has a length of 50. You can change the length in table design view or column properties.
Collation
Collation can be specified at the instance level, database level, and even down to the column level. This property displays the collating sequence that SQL Server applies to the column. To change the collation using column properties, click the ellipsis and choose the collation:
Computed Column Specification
Computed Column Specification displays information about a computed column. A computed column is a logical column that is not physically stored in the table unless the column is marked as Persisted (see Is Persisted below)
- Formula: This field is where you can use formula’s. (See below for an example)
- Is Persisted: This field indicates whether the results of the formula are stored in the database or are calculated each time the column is referenced
Click here to view the rest of this post.